Location
Type of project

Arbonaut developed a mobile application Tassu, designed to streamline field inspections. Tassu plays an important role in supporting the Finnish Forest Centre in monitoring legislative responsibilities for private forests. This means, for instance, monitoring different forest operations or the implementation of subsidized improvement projects.

Arbonaut continues to work with the UNDP, the National Forest Authority and the National Environment Management Authority in Uganda to bring forth a methodology for wetland monitoring. The current Uganda National Resource Information System NARIS (developed by Arbonaut previously) will be scaled up with new datasets and tools, allowing users to map and monitor wetland occurrence and wetland cover change. The development of this new functionality within NARIS will be concluded with capacity-building activities, such as user training on the upgraded platform and training on wetland change mapping using NARIS and remote sensing-based methods.

Arbonaut, Metsähallitus and Triona are collaborating in the implementation of a new platform Kaira. The system will streamline forest and nature management projects, enhance the quality and monitoring of the process, as well as support Metsähallitus' decision-making capabilities. Kaira will emerge to replace Silvia (developed and maintained by Arbonaut) in 2025 to handle the state forest management in Finland.

Arbonaut collaborated with the Zambia Timber Auction Floor to pave the way for localizing a ProMS solution. The new GIS system will help to better monitor land concessions and safeguard forests in Zambia. It will support forest concession holders in increasing productivity throughout the entire timber procurement chain. The project aims to significantly improve the amount of data that ZTAF possesses about their land and will impact forestry sector as a whole. Supported by Finnpartnership.

Arbonaut partnered with Face the Future from the Netherlands to conduct the Carbon, Social and Biodiversity Impact Assessments according to the VCS and CCB standards and to develop a monitoring system for the Forest Restoration Project for Carbon Absorption in Uganda. The 20-year project is funded by VELUX and implemented by WWF Uganda and National Forest Authority in the Albertine Rift Landscape. Arbonaut’s experts lead satellite-based remote sensing and spatial analysis activities.

Arbonaut and a local partner Environmental Tracking Foundation is in the process to comprehensively assess the quantities and quality of the wood stock in the exotic forest plantations to the Zambia Forestry and Forest Industry Corporation PLC. Our team is delivering a forest resource inventory, a five-year forest management plan and the Forest Information Management System followed by the user training of the ZAFFICO’s key personnel.
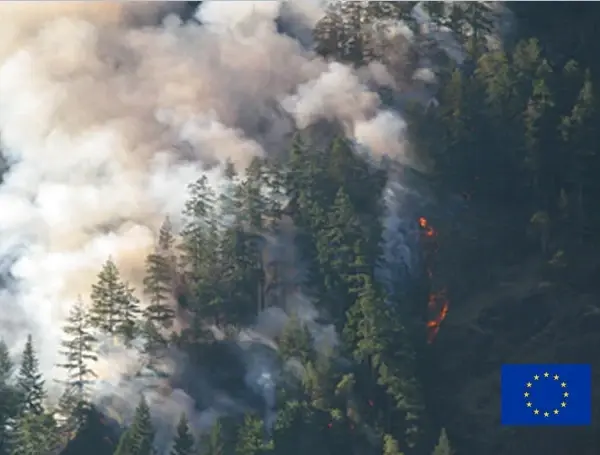

Arbonaut is a proud member of the FirEUrisk consortium established within an EU-funded Horizon 2020 program aimed at developing a holistic, risk-wise strategy for European Wildfire Management led by the University of Coimbra with a budget of 10 million euros. Arbonaut is in charge of integrating FirEUrisk resources with other EU platforms and legacy systems and guiding the development of the public cooperative platform. A tool based on our ProMS solution will be built to display project outputs in a unified user interface on the web and mobile devices. The team will take part in carrying out fire danger assessments, risk-wise landscape, and fuel model development to reduce the probability and potential of ignitions.

ReCover project aimed to develop beyond state-of-the-art service capabilities to support fighting deforestation and forest degradation in the tropical region. The service capabilities mean the provision of a monitoring system of forest cover and forest cover changes and biomass which includes a robust accuracy assessment. The capabilities were based on mainly spaceborne earth observation data and in-situ data. The project was funded under the Framework 7 Theme Space program of the European Commission. The consortium consisted of nine leading research and industrial partners, Arbonaut being the only SME representative. The service development was controlled by specific user requirements that were expressed through Service Level Agreements between the ReCover consortium and users in Mexico, the Democratic Republic of Congo, Guyana, Fiji, and Colombia.
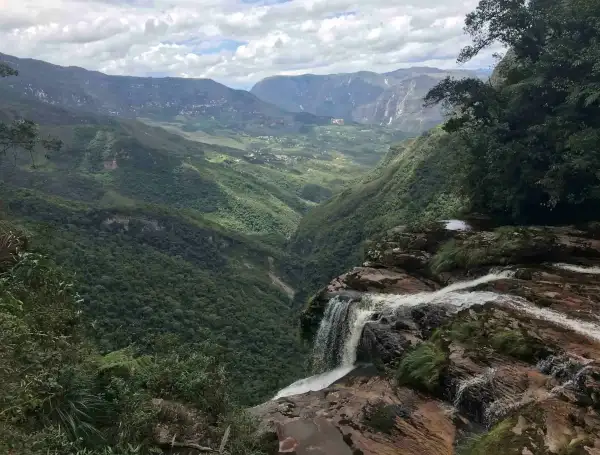

Arbonaut provided expert services for developing a mobile application for forest inventory data collection for FAO. The inventory expert prepared and delivered a field training program in Peru. The baseline version of Collect Mobile was developed as part of Arbonaut’s contribution to the Open Foris Initiative. Arbonaut continues to support the implementation of the Open Foris Collect 3.0-based Open Foris Collect Mobile Application for Android Operating Systems.
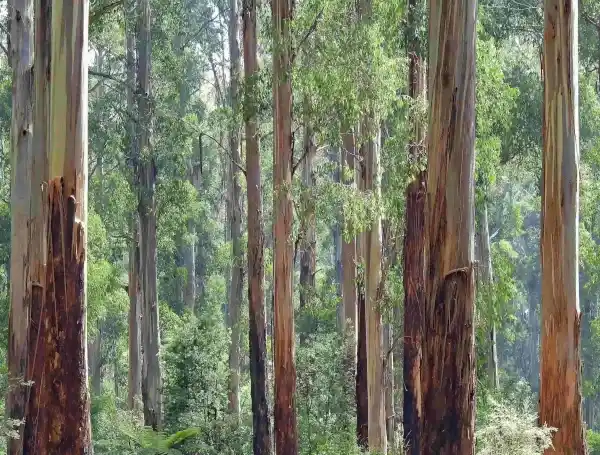

Arbonaut and a local consultant Estudio Forestal Faroppa implemented a LiDAR inventory for two private forestry companies. The inventories were focused on selection of stands representing all stands in inventory rotation of forestland in 9 municipalities across Uruguay. Arbonaut calculated timber inventory based on the LiDAR data in combination of an area-based approach and individual crown identification to acquire high accuracy on stem count and mean tree volume. As a result, the customers received accurate, timely, and targeted inventory results while obtaining services that are economically sound on an operational scale.
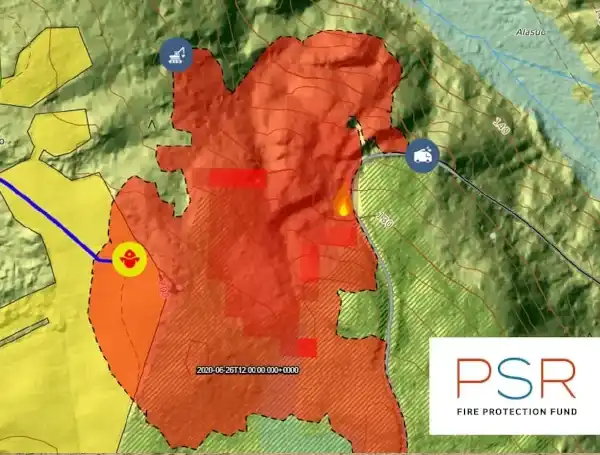
Arbonaut and the Finnish Meteorological Institute finished a forest fire management-related project MAST 2, which originated from a previous MAST project. The goal of the project was to improve the Prometheus fire simulations and user interfaces of the models predicting forest fires in Finnish conditions. It included the development of a feature that would consider the effects of firefighting measures of fire crews and any terrain changes in fire spread forecast. Funded by the Fire Protection Fund (Palosuojelurahasto).
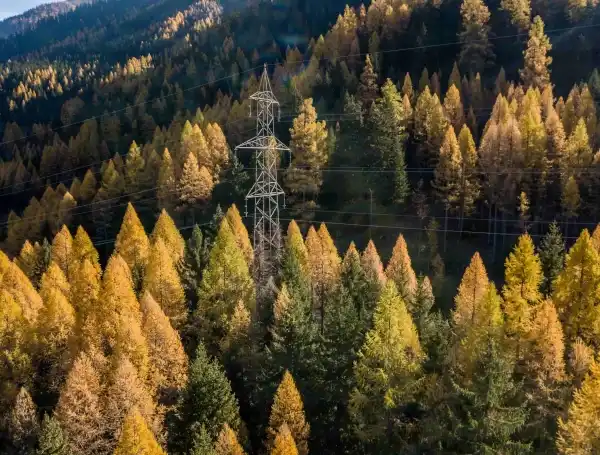

Arbonaut carried out multiple work assignments related to corridor mapping for the Utility Risk Management Corporation in the USA. The 5-year assignments included analysis of LiDAR data on vegetation and powerlines, polygonization of tree crowns, LiDAR classification, and detailed vegetation and infrastructure modelling. While delivering Arbonaut’s methods to the largest electrical transmission owners (American Electric Power, Duke Energy, Entergy, and First Energy Dominion Virginia Power) we created common industry phrases and deliverables which are now written into the best practices in the North American transmission grid.

Arbonaut and Forestry Club de France have been selected as winners of the 7th call for the "Give relief to your projects with the LiDAR" project by IGN. Arbonaut is developing a solution for assessing the health of forests using data from the HD LiDAR campaign. The objective of the project is to help French forest owners set up and optimize the monitoring of their forest health by taking into account different risk factors. This solution will become available to all forest owners and managers.

Arbonaut developed a mobile application Ahma for the Finnish Forest Centre to assists them in checking and updating information on environmentally important habitats and forest resource data in the field. Users can conveniently assess the quality of forest resources and operation data produced by a remote sensing method directly in the application.

Arbonaut was a lead Nordic partner in the project aiming to provide affordable, renewable energy and create employment, well-being, and revenue opportunities for the local communities in the Sarlahi and Mahottari districts. The project was done together with a local partner Bakas Renewable Energy. To replace coal and firewood in small industries and households in Nepal and to reduce greenhouse emissions, the sustainable production of biomass wood pellets on an annual basis was implemented with a newly built pellet factory. Arbonaut developed a GIS-based web and mobile app with all the relevant data like LiDAR-based forest inventory, terrain, forest fire risks, and weather to sustainably manage biomass resources, harvest planning, and assess forest fire risks. The end-users took an active part in the app testing process and user training. Funded with the Nordic Climate Facility grant financed by Nordic Development Fund.

Arbonaut developed a custom-built QGIS-based application Luoto for the Finnish Forest Centre that supports the planning of nature management projects. Nature management projects include the maintenance and renovation of environmentally important habitats, rehabilitation of forests and peatlands, as well as prevention and repairs of water damages caused by ditch activities. The Finnish Forest Centre uses Luoto’s maps and planning tools to delineate the nature management project areas, create activity plans, and prepare materials for public tendering for organizations to implement them.

Partnered with the University of Helsinki and Tampere Vocational College Tredu, we tested innovative, already developed methods that recognize ecological aspects of forests while logging, leading to better logging decisions and less environmental burden on forests. Arbonaut tasks included remote sensing-based dead tree detection and the creation of tree map data, which is described in such a way that every tree has coordinates and other tree-level attributes, like its species, height, and diameter.
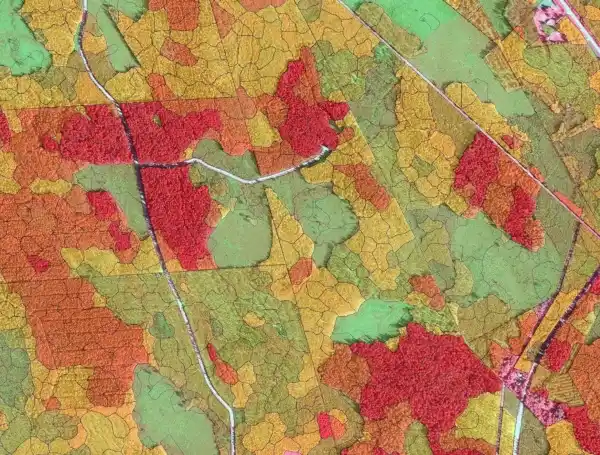
Arbonaut and a partner Vivid Economics were appointed by Forestry and Land Scotland to carry out airborne laser scanning of Scottish forests in Dumfries and Galloway. The Scottish Airborne LiDAR Tool for Inventory and Resource Estimation (SALTIRE) aimed to improve resource planning by increasing the quality, coverage, and accuracy of the forest information that FLS holds. Arbonaut used an innovative modeling approach that combines individual tree estimates with area-based approaches to improve the accuracy and precision of the forest inventory results. The project was a part of the CivTech Programme 5.0 Accelerator designed by the Scottish government to promote innovation in the public sector.

The MARISKA project was a follow-up of the MAST and MELLEVÄ fire-related projects that Arbonaut had implemented in the past. This project was a joint effort of Arbonaut with the Finnish Forest Centre and Emergency Services Academy of Finland. Arbonaut produced static fuel maps for the whole of Finland so that Finland can prepare for future forest fires prevention and suppression and support firefighting work. Funded by the Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry.

Dead trees are an essential part of forest biodiversity and serve as biodiversity indicators. It is important to consider dead tree groups in forest operation planning, for example, by leaving standalone trees or protected areas in the dead tree groups. However, dead tree material may also increase some risks like wildfires and insect damage. Arbonaut and the Finnish Forest Centre tested new methods to automatically detect standing and fallen dead trees in forests with LiDAR data. The measurement techniques developed in the Kuopus project will allow consideration of dead trees in forest management decisions.

Arbonaut was an innovator in the Climate Innovation Challenge of the Asian Disaster Preparedness Center. In this awarded project, Arbonaut and a local partner Clean Energy Nepal developed and piloted a GIS web-based platform and mobile app for local farmers in Nepal and focused on building food security in the farming communities. CIC focuses on the crowdsourcing of disruptive technology solutions to build communities’ resilience against the threat of climate change in South Asia. The CIC is an essential part of the "Climate Adaptation and Resilience for South Asia" project administered by The World Bank and funded by the UK’s Foreign, Commonwealth and Development Office.
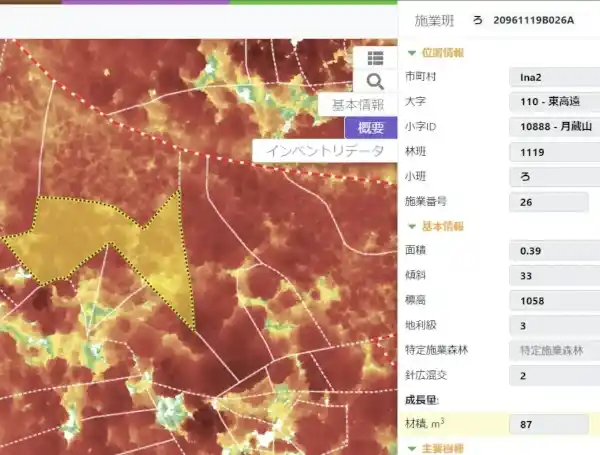
Together with a local partner Precision Forestry Measurement Ltd (PreFore), Arbonaut team has been developing a Forest Resource Management System that serves in Japanese condition (piloted in Nagano prefecture). Japan is widely covered by forest and has mountainous terrain. With the abundant forest resources ready to be harvested nowadays, challenging topography requires well-planned forest operation based on digital data to be profitable. To support efficient operation planning and management, the ForPas system will allow non-specialist forestry staff to easily use and share the forestry data within both national and private forest schemes.

The BIOKARELIA project aimed at the development of practical tools for biodiversity hotspot preservation via mapping biodiversity values and monitoring and forecasting the occurrence of forest fires and wood harvesting along the Russian-Finnish border. It was a collaboration of three organizations from Finland (Natural Resources Institute Finland, Centre for Economic Development, Transport and the Environment of North Karelia, and Arbonaut) and three Russian organizations (Lesnoe Bureau Partner, Forest Research Institute of Karelian Research Centre, and Kostamuksha Nature Reserve and Kalevala National Park). The BIOKARELIA project was a part of the Karelia CBC-Programme. The Programme is financed by the European Union, the Russian Federation and the Republic of Finland. More information from the project website: kareliacbc.fi
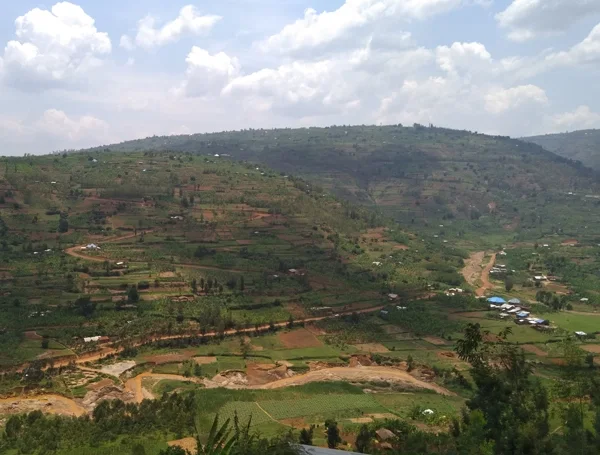

Arbonaut, together with partner KartECO, assisted Rwanda Forestry Authority in the development of a Forest Monitoring and Evaluation System. The main purpose of the system was to provide national and district-level information on the key forestry sector indicators of Rwanda, to the RFA and stakeholders. The FMES system was integrated into the newly developed District Forest Management Plans system, and it included functionalities for collecting, calculating and reporting the indicator data.
Donor: Belgian Development Agency: Enabel.
Arbonaut developed a custom-built QGIS-based application for the Finnish Forest Centre called Koala designed for planning field plot measurement campaigns, data post-processing, and quality control of remote sensing-based forest inventory. Koala is part of a renewed forest resource information system used by the Finnish Forest Centre in daily operations. It supports them in achieving an ambitious target to annually collect the data for 22 inventory areas with 200,000 ha of forest per area. Arbonaut is also responsible for the system maintenance that started in May 2022.
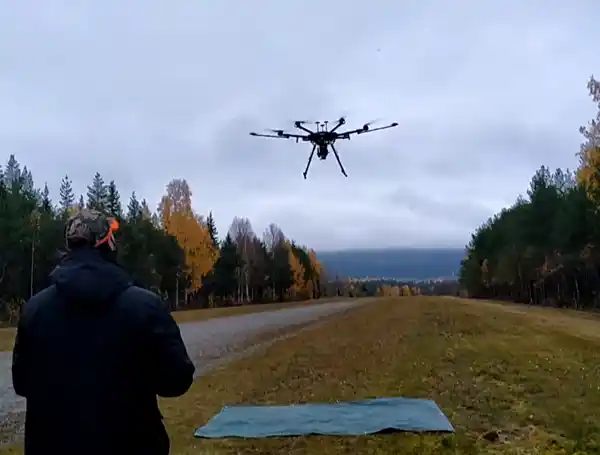

Digitalization of the field inspection process called for new methods and technologies. Arbonaut collaborated with CareliaForest Consulting Oy and focused on drone technologies for collecting and analyzing forest inventory data in small forest areas. This project for the Finnish Forest Centre involved 600 stands with an average of 2 hectares each. High resolution RGB aerial images collected with drone were used to produce photogrammetric point cloud and ortho mosaic. Area delineation, harvesting tracks and possible other interesting objects (snags, fallen dead trees) were detected using visual interpretation.

The project was designed to build urban resilience and support climate-adaptive planning in Nepalgunj Sub-Metropolitan City and Birendranagar Municipality of the Mid-Western Region of Nepal. The project helped to increase resilience to climate extremes and disasters such as drought, flood, inundation, and landslide. With the support from the local partners Oxfam in Nepal and Clean Energy Nepal, Arbonaut was a Lead Nordic partner and successfully conducted Vulnerability Assessment for Nepalgunj Sub Metropolitan City using GIS data and visualized the assessment in interactive maps in the ProMS platform. The project was funded with a Nordic Climate Facility grant by Nordic Development Fund.
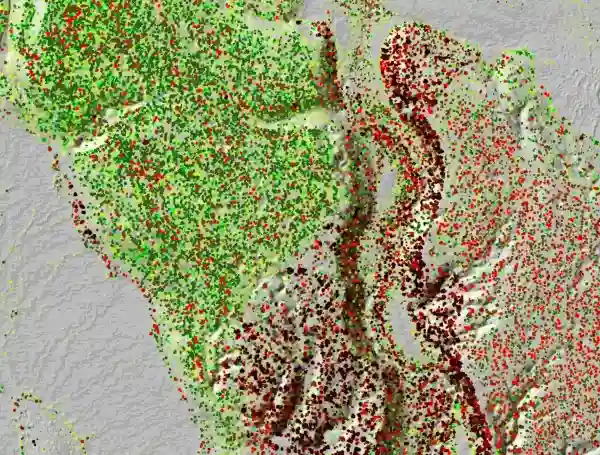
Arbonaut and MW Group's subsidiary MW Forest Sense developed a unique forest ecosystem inventory solution for Jokkmokk Allmänning in Sweden. Modern LiDAR sensors provided a detailed digital twin of the forest ecosystem for the customer. The project covered three main aspects: timber inventory made on crown polygon level, environmental analysis of the biodiversity and ecological values, and analysis of the operating conditions allowing to do an extensive part of logging planning work from the office. This project is showing the benefits of digital forestry by providing Jokkmokk Allmänning with highly accurate data to make ecologically and economically sound decisions on forest management.

Our team is developing the Cambodia Environmental Management Information System (CEMIS) platform to serve as a Decision Support System by assessing conservation priorities, zoning of the protected areas, and allocation of land for environmental management purposes. The project will be finalized with training for the Department of GIS under the Ministry of Environment of Cambodia so that its staff will become well-versed users of the CEMIS platform. The project is supported by the UNDP and implemented in collaboration between Arbonaut and partners: GIS laboratory for a Management Information System from UNDP, USAID Greening Prey Lang, SERVIR-Mekong Geospatial Tools, and Services Development in Cambodia of USAID, and Asian Disaster Preparedness Center. In addition, the CEMIS is a part of The World Bank’s 'Cambodia Sustainable Landscape and Ecotourism project’ (CSLEP).
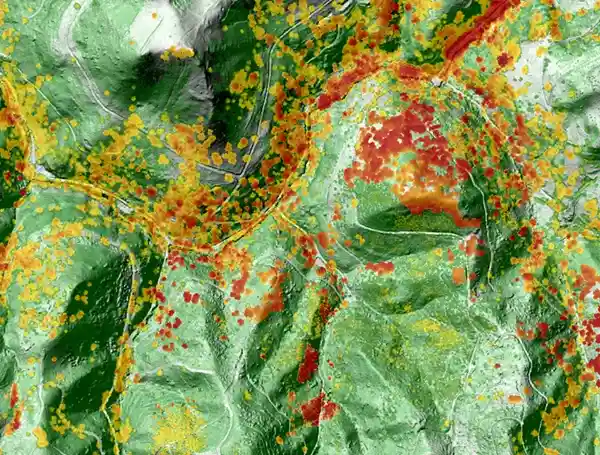

Arbonaut closely worked with ForestWISE and the Portuguese government to develop a solution for wildland and wildland-urban interface forest fire management. The project was implemented in Pombal, PF Monsanto, Mafra, Serras da Lousa, PN Sintra Cascais, VPA, and Proenca-Oleiros, covering a total of 45,165 ha of land. Arbonaut carried out mapping of vegetation and conditions for wildfire management with LiDAR and other remote sensing data. Fuel and topographic data can now be accessed through ProMS helping to make timely decisions for fire prevention and suppression. The solution also provides valuable information on fuel conditions around infrastructures (roads, houses, and other buildings), i.e. defensive perimeter, fuel statistics within a certain perimeter and classification of infrastructures according to the risk.

The MAST project used forest fire R&D from different countries and adapted them to Finnish conditions and needs. In the project, more effective methods for creating situational awareness for managing rescue operations in case of wildfires were developed. The interpretation of forest information used the algorithms previously developed by Arbonaut for the LiDAR data interpretation. The Finnish Meteorological Institute integrated a wind model, which enabled accurate predictions of the spread of wildfires. The new models were studied and tested by the Emergency Services Academy Finland and the North Karelia Rescue Department as part of rescue operations management. Financed by Palosuojelurahasto (the Fire Protection Fund).
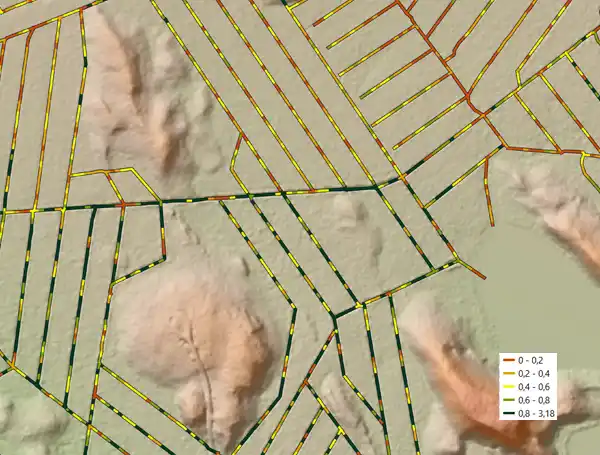
Arbonaut, in collaboration with TAPIO, the Natural Resources Institute of Finland, and the Finnish Forest Centre participated in a project that contributed to sustainable drainage management practices in Finland. HYTKY aimed to optimize the carbon sinks on peatlands, considering carbon balance on soil and trees, particularly with the precise planning of drainage. Ditch depth results, along with other additional input data are integrated into a SUSI simulation model, produced by LUKE to predict various effects of groundwater level in forest growth and carbon balance from soil. Arbonaut’s project management platform ProMS hosts spatial data from the test areas with background data. Funded by the Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry's Carbon Climate Action package for 2020.

Arbonaut signed a contract with the Nigerian Forest Carbon Partnership Facility REDD+ Programme of the Federal Ministry of Environment to lead a project aiming at the operationalization of the National Forest Monitoring System in Nigeria. Together with the Nigerian Conservation Foundation as a sub-consultant, Arbonaut assisted Nigeria in the development of the Standard Operating Procedures and supported technical teams in testing the NFMS implementation. The project was financed by the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development through the Forest Carbon Partnership Facility of the World Bank.

Accessibility of forest resources plays a major part in operational planning and operational costs in the forestry sector, both in Finland and even more so in Russia. Traditional methods of collecting forest road data by visual inspections and manual measurements are often expensive and not accurate enough. Hence, the specific objective of the Access2Forest project was to develop advanced planning technology for forest logistics and forest road construction and maintenance planning in a cross-border bioeconomy. The Access2Forest project was a part of the Karelia CBC-Programme financed by the European Union, the Russian Federation, and the Republic of Finland.
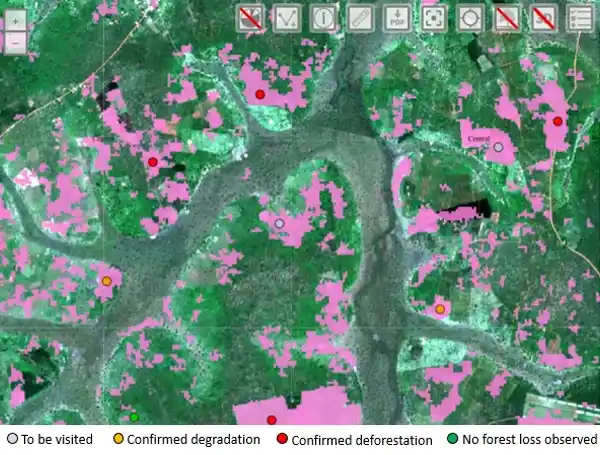
Arbonaut implemented Uganda National Resource Information System NARIS, a data visualization and sharing platform. It was created for the National Forest Authority to monitor forest cover changes in Uganda. Arbonaut contributed technical assistance to developing the web and mobile platform which integrates field observations, remote sensing data, and data validation tools. The platform contains the latest map layers showing the rate of land use change and forest cover loss in a selected pilot region in Uganda. The platform harmonizes the different data sources and facilitates decision-making for effective forest management and prevention of deforestation and forest degradation.
About the project from UNDP Uganda’s website: undp.org/uganda.
Donor: United Nations Development Programme (UNDP).
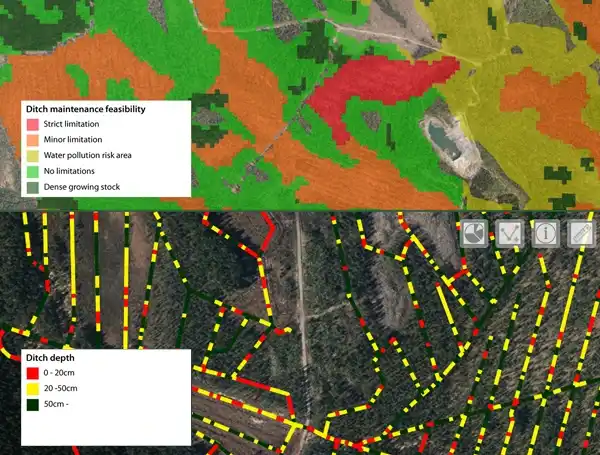
Arbonaut developed a five-level system for project sustainability assessment in drainage management for Metsähallitus Forestry in Finland. Multiple factors (groundwater, drainage, forest fertility, relics, ecological and conservation areas, etc.) were used as input layers and included in the analysis, producing data that aids customers’ decision-making regarding ditch maintenance operations. Arbonaut analyzed the ditch depths so that the areas that are in the most urgent need of maintenance could be efficiently identified. The ditch depth evaluation was done based on a digitized ditch lines and LiDAR data collected by the National Land Survey of Finland. The analysis was done in 8-meter intervals and presented with a three-level system, which helps in quick visual assessment of shallow ditch lines.
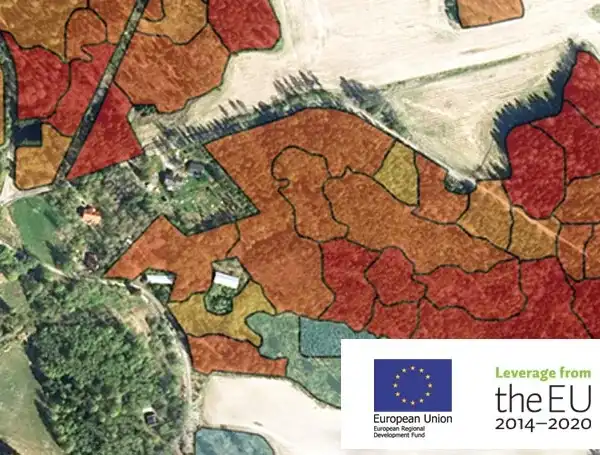
Arbonaut collaborated with Lapland University of Applied Sciences, Karelia University of Applied Sciences and Tapio Silva Oy to further develop a Virtual Forest tool for forest data 3D visualization that combines forest data with spatial data. Virtual Forest can be used in forestry education, land use planning, forestry, and timber procurement. During the Virtual Forest 2.0 project, Arbonaut produced simulated maps that enable realistic visualization of forests.
The Virtual Forest 2.0 project was led by the Lapland University of Applied Sciences and financed by the European Regional Development Fund. More information from the European Union EURA2014 portal: eura2014.fi

Arbonaut and a subconsultant Green e-Solutions assisted the Department of Forest and Park Services of Bhutan in the development of a GIS-based spatially-enabled knowledge base and Decision Support System (SDSS). The system comprised of a nationwide spatial database, portal, and a decision-support tool kit built from open-source products to facilitate informed, unbiased and expeditious decisions on forest clearance. The SDSS provides GIS analysis and appraisal of forestry clearance project proposals and delivers results of analysis to issue forestry clearance based on set criteria and rules within a few minutes.Donor: Forest Carbon Partnership Facility (FCPF) and the World Bank.
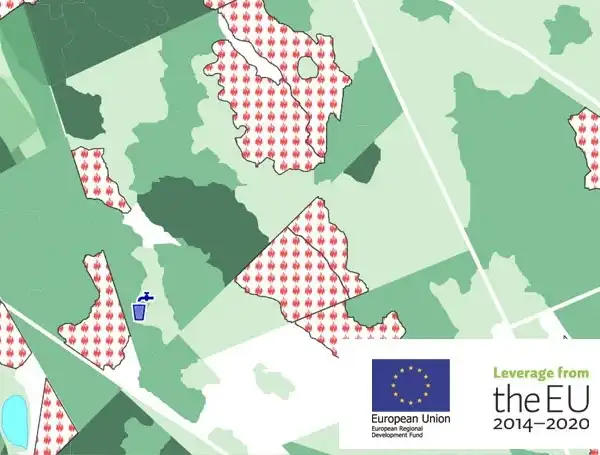
The Mellevä project aimed to create a mockup demo for supporting forest fire prevention by using forest inventory data and online weather data. The demo was based on an earlier development project during which Arbonaut constructed a LiDAR-based fire prevention map of the Lieksa area in North Karelia, Finland. The Mellevä demo illustrated the benefits of a Decision-Support System (DSS) for forest firefighting in Finland for rescue departments. In addition to the national development, the project allowed research opportunities for forest fire know-how export outside of Finland in the future.
The project was led by the Finnish Forest Centre and financed by the European Regional Development Fund. More information from the Finnish Forest Centre’s website: metsakeskus.fi/melleva

The Digitally Connected Forest Operation Value Chain (ForOps) project aimed at the development of a new digital platform for enhanced cooperation between forest service providers, individual entrepreneurs and forest owners. The end product aids in the division of work in the forestry sector and improves the overall capacity to manage and maintain valuable forest resources in East and North Finland. In ForOps project the main goal was to develop the ProMS platform to be used as a “forest work bank” for general silvicultural work assignments, tracking, and reporting. Together with the project partners Lapland UAS and Rajaforest, the new platform was tested in a real operational environment. The solution can also be used to manage forest road maintenance planning and management, as well as multiple uses of the forest.
Financed by the European Commission within the ELMO High Impact Action pilot: elmoenf.eu
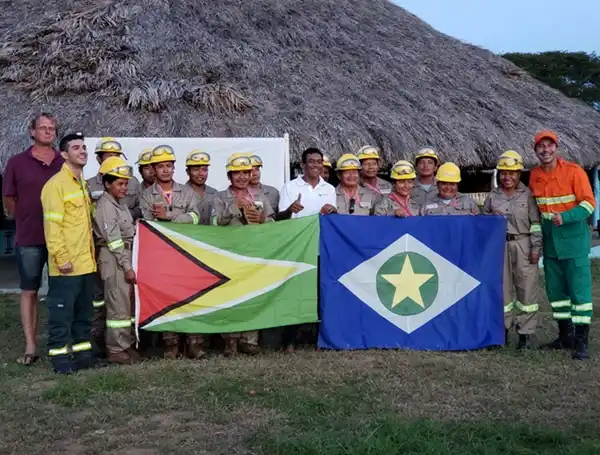

In partnership with FCG International Ltd, Arbonaut supported REDD+ Guyana to prioritize, design and implement three REDD+ pilot projects in consultation with stakeholders while considering the REDD+ Strategy and SESA for Guyana. The activities included supporting the implementation of a Village Improvement Plans, Fire Protection Plans and Suppression of Fire, development of Alternative Income Projects for Forest Dependent Communities, and development of MRV systems. Donor: Forest Carbon Partnership Facility and the World Bank.

During the project, PRONG received training and technical capabilities to support actors in eight countries in West Africa. By providing them with open-source technology-based spatial information systems, more effective implementation and monitoring of environmental and development policies had become available. The states’ capacity in forest monitoring and for action under the REDD+ program improved, resulting in a reduction in deforestation and more secure monitoring of carbon sinks. Funded by Finnpartnership, a business partnership programme financed by the Ministry for Foreign Affairs of Finland and managed by Finnfund.
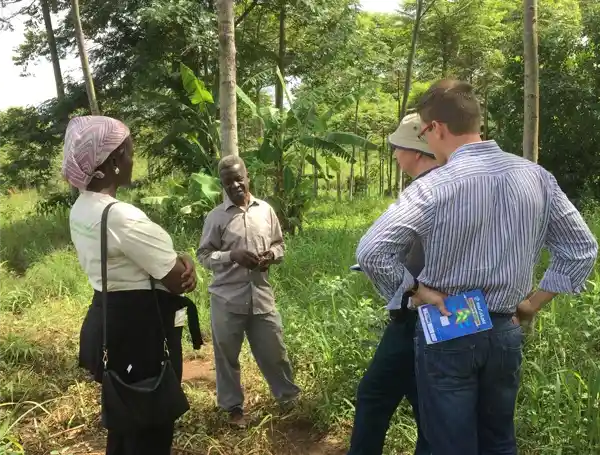

Arbonaut contributed to Uganda’s REDD+ Readiness process by developing a Safeguard Information System (SIS). During the project, Uganda’s REDD Strategy implementation approach was further reviewed, showing how to roll out REDD+ across the country and how the overall approach to the ER Programs was to be conceptualized. Arbonaut also developed the Process Framework, Indigenous Peoples Planning Framework and Resettlement Policy Framework for Uganda’s National REDD+ Program. The SESA report and ESMF were also reviewed. As an Addendum to the project, Arbonaut team developed Safeguards Instruments (PF and ESMF) for the Forests and Resilient Landscapes Project of Uganda.

The ECO-Bridge project aimed at increasing environmental awareness and improvement of people's living environment through the introduction of joint approaches and principles to environmental monitoring in Finland and Karelia. Accurate real-time data about water and air quality to be comparable between Finland and Karelia did not exist, so better management of transboundary environmental data was needed. The outputs of the project included: (1) Action Plan for sustainable operation of joint environmental monitoring in transboundary areas, (2) modernized monitoring network and facilities in the pilot territories, (3) platforms for monitoring data exchange on both sides of the border, and (4) higher level of knowledge of the employees of partner organizations in modern requirements, methods, and technologies for further development of the environmental monitoring systems
More information: kareliacbc.fi
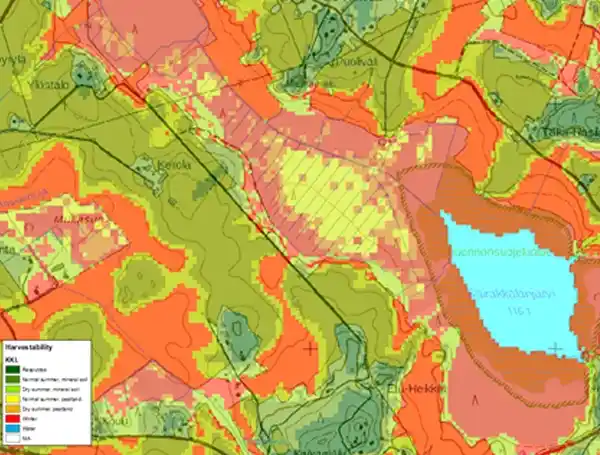
Together with Metsäteho, its stakeholders, and the Finnish Forest Centre, Arbonaut had been developing forest trafficability maps since 2014. The trafficability maps provide information on soil load-bearing capacity and enable better recognition of logging sites suitable for year-round wood harvesting. The maps ensure less damage to soil and the remaining trees, less unnecessary transfers of forest machinery, and the effective planning of logging operations in a timely manner. The analysis was done with airborne laser scanning data and a topographic database provided as free data by the National Land Survey of Finland. The method can be applied in other countries where input data for analysis is available.

SUFOGIS aimed to respond to the needs identified by the promotion of sustainable forestry and ecology in Russia and China through improved university-enterprise cooperation and enhancing the skills and competencies of students and professionals. The project focused on capacity building in the fields of GIS and remote sensing in higher education institutions in partner countries. The short-term goals were to train staff from the Russian and Chinese organizations, coordinate summer courses in order to educate Russian and Chinese students, develop knowledge transfer guidelines, and equip the proposed centers.
More information: sufogis.volgatech.net
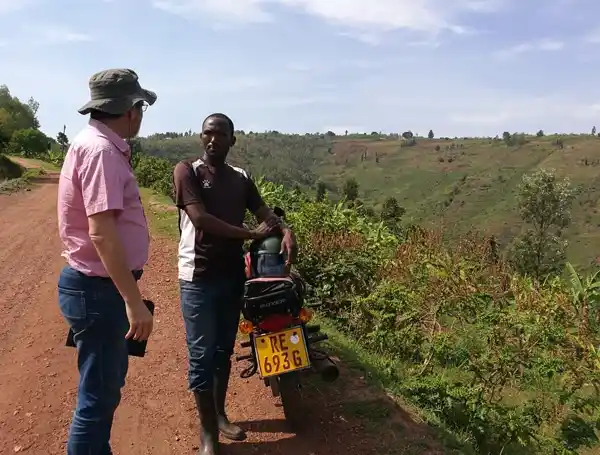

Arbonaut, together with partner KartECO, assisted Rwanda Forestry Authority in the development of a user-friendly and customized District Forest Management Plans (DFMP) system for collecting and managing stand-level forest resource and forest management planning data. The DFMP system has been supported the central and district-level officers to easily design, implement, monitor, and update district forest management plans for each district of Rwanda. The system includes a centralized database, web platform, and mobile application for fieldwork and reporting functionalities.Donor: Belgian Development Agency Enabel

The risk for forest and wildland-urban interface fires is acknowledged to increase as the climate is getting warmer affecting forest land managers and the general public. Hence, the Fire Brake micro-project aimed to improve knowledge and collaboration in the field of forest fire risk assessment and management between Finland and Russia. By researching different entities operating with forest fire risk management and their challenges from both sides of the border, it was possible to identify the bottlenecks and areas that need further development and capacity-building actions. In this project, Arbonaut collaborated with the natural protection, research, and environmental education establishment Vodlozero National Park.
The Fire Brake project was a part of the Karelia CBC-Programme financed by the European Union, the Russian Federation and the Republic of Finland. More information: kareliacbc.fi

The Logroad micro-project aimed to identify and solve problems related to the construction of forest roads, which have a negative impact on timber industry development on both sides of the border. New approaches and technologies to planning the construction of forest roads facilitated the competitiveness of the logging, transport, and timber industries. In this project, Arbonaut collaborated with a forest inventory and forestry planning specialist from Lesnoe Bureau Partner.
Logroad project was a part of the Karelia CBC-Programme financed by the European Union, the Russian Federation, and the Republic of Finland. More information: kareliacbc.fi

Arbonaut developed an operational system for assessing water quality in Finnish lakes and coastal waters within the Data Fusion Project of the Finnish Environment Institute (SYKE). The system is used both for real-time monitoring of the water quality, as well as for redoing analyses of past events, e.g. algal blooms. The implementation of the project included specification of the system, development of the system components for data download, harmonization, fusion and post-processing, and training of the client’s staff and customers for operation and maintenance. As a result, the data fusion system allows SYKE to estimate variables related to water quality proactively, automatically, and in real time.
More information: syke.fi

The purpose of the FORMIS II project was to develop a fully integrated Management Information System for sustainable management of forest resources and, in this way, contribute to the alleviation of poverty in the socio-economic development framework of Vietnam. Arbonaut finalized and improved one of the key systems of FORMIS, namely Forest Resource Monitoring System (FRMS) for the Vietnam Administration of Forestry. The FRMS was deployed to all districts to store and keep stand level forest resource data up-to-date and to monitor forest cover changes nationwide. Donor: Ministry of Foreign Affairs in Finland.

Arbonaut, in collaboration with the Perm State University and Center for Space Technologies, worked on the adaptation of LiDAR-based forest inventory methods to fit the requirements of the Russian legislation and the needs of the industry. Further Russian partners carried out forest inventories by using ArboLiDAR tools and with the support of Arbonaut's experts.

Arbonaut and the IUCN-Uganda contributed to Uganda’s REDD+ Readiness process by developing Uganda’s National REDD+ Strategy. Arbonaut developed the Strategic Environmental and Social Assessment (SESA) and Environmental and Social Management Framework (ESMF) for Uganda’s National REDD+ Program. During the project, potential strategic options were identified and assessed to meet international guidelines and national safeguards. The assessment was compiled into a REDD+ Strategy Options Paper that worked as a basis for full and effective consultation and the preparation of the REDD+ Strategy and a Costed Action Plan. The Strategy was launched in November 2017 during the UN Climate Change Conference (COP23) in Bonn, Germany.

EFFORTE was a research and innovation project providing the European forestry sector with new know-how to significantly improve the assembling and adaptation of novel technologies by forest enterprises. The project aimed at enhanced efficiency in forest operations, sustainable forestry, increased forest growth, cost-competitive bio-based industry, and acceleration of regional economic development. The project was based on three key elements: (1) an understanding of soil mechanics and terrain trafficability, (2) potential of mechanization in silvicultural operations, and (3) ‘Big Data’ to increase the efficiency of forest operations.
EFFORTE had received funding from the Bio Based Industries Joint Undertaking under the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 720712. More information: luke.fi/efforte

The project aimed to support local entrepreneurship and reduce deforestation and mitigate greenhouse gas emissions by introducing Non-Wood Forest Products as an alternative to agricultural production as the main livelihood in the rural community of Bandafassi. The underlying objective was to limit the impact of degradation factors on Niokolo Koba National Park, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, and ensure the regulation of the flows of major rivers Niger, Senegal and Gambia. Bandafassi consists of 33 villages and 2,300 households. A REDD+ MRV methodology and system were developed and piloted in the project. Financed by the Nordic Development Fund of the Nordic Climate Facility.

Arbonaut was working in an international consortium targeting the identification and prioritization of strategic options to address the causes of deforestation and forest degradation in Ethiopia. Some of the project activities included: (1) assessment of the magnitude and impact of underlying causes and drivers of deforestation in the four regions of interest, (2) spatial analysis of the LULC, (3) assessment of potential for increased carbon removal through reforestation and afforestation of previously degraded lands, (4) future scenarios to address the identified present and future causes of deforestation and forest degradation for increased carbon removals, and (5) a roadmap for the national REDD+ Strategy and Synthesis.
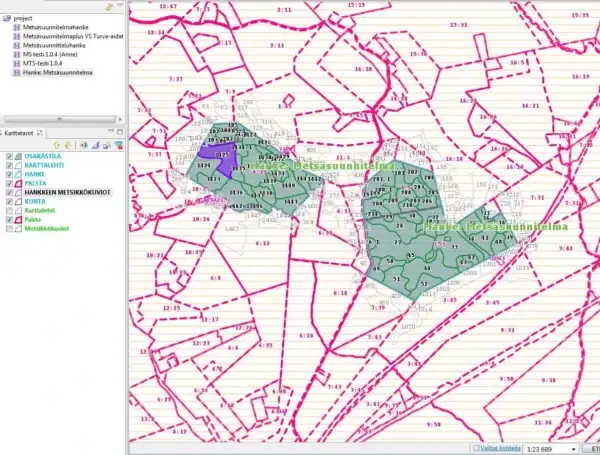
MörGIS system was a fully autonomous, critical and central tool for OTSO Forest Services, a private Finnish company operating and servicing forest land owners, municipalities and other private or governmental authorities. MörGIS was used daily by around 400 users to manage over ten business processes, the majority of these being automated in the GIS system to cover all forest management activities and help to serve OTSO Forest Service's customers in an efficient and modern way.

Arbonaut developed a waste biomass potential map for the selected states based on a state-level land-use map for five land-use types and quantified uncertainty in relation to spatial distribution. A more detailed land-use classification was developed for six smaller pilot areas where the best available land use methodologies were studied. The selected states were Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra and Tamil Nadu. The total pilot area was larger than 730 000 km². Funded by TEKES (the Finnish Funding Agency for Innovation).

Jahtipaikat is a paid web-service including an online store implemented for Metsämonex Oy. With the service, hunting clubs can manage their members' data, save and edit hunting leases as a hunting form for each property, as well as print out the necessary maps and reports. The purpose of the service was to support the club secretary in an office, yacht master planning and hunters during a hunt. The users can keep the due date of a book by adding and editing items such as hunting stand locations, meeting points, or even game cameras location. There was also a mobile-optimized version of the service, which could take advantage of GPS functionalities to allow following the hunt.
FORMIS supports Directorate of Forestry under the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development in sector-wide forest governance and management by developing a modern information system from the central to the local level in order to provide accurate information for decision-making in the forestry sector at all levels. The project covered a national level and three provinces: Thanh Hoá, Thua Thiên Hué, and Quang Ninh. Funded by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Finland.
Metsäsoppi was a web service that enabled controlling forest management plans of the UPM contract customers. The platform contained geographic information layers, interfaces to UPM’s forest information system and reporting features, which allowed presenting information about forests and service use statistics. The user could automatically print out forest management plans including thematic maps in PDF format from the selected forest properties and stands. Metsäsoppi allowed making notes for forest taxation and printing out tax return forms filled by the system. The system also allowed electronic submission of the forest tax clearance with OpenID Connect- and Katso-identification directly to the tax authority system in Finland.
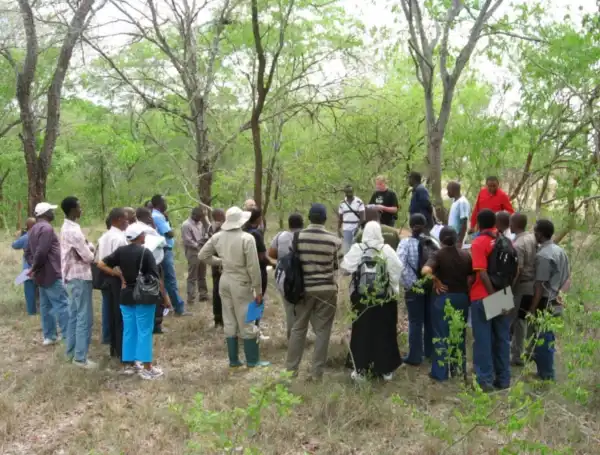

Together with local trainers at Sokoine University of Agriculture, Arbonaut held a 2-week training in Morogoro with the support of the Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation and Mitigation Programme. Arbonaut delivered lectures, demonstrations and practicals about processing and integrating LiDAR data and ground-based inventories for forest biomass mapping and assessment.
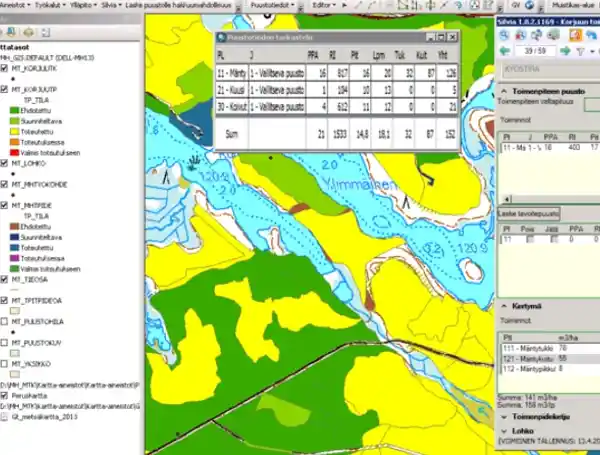
Silvia was a central GIS system for Metsähallitus for forestry and silvicultural operations like logging and forest road network maintenance planning. Metsähallitus manages commercial forests as multiple-use forests in which special emphasis is put on recreational use parallel to timber production.

Technologies introduced in the Energy and Environment Partnership Programme's project included biomass monitoring and the annual harvest planning system for the sustainable supply of renewable energy integrating low-cost, readily available mobile data collection and modern cloud computing tools. These technologies actively engaged the communities with community-based forest monitoring and community-managed charcoal production centers. The solution was transferred to MIME and the Forestry Administration and in the future, the solution can be easily and directly replicated by other forest management agents and charcoal-producing communities outside the project's scope.

Arbonaut developed a forest inventory methodology for the Forest Preservation Programme in Ghana. The Forest Preservation Programme, funded by the Japanese Government and receiving technical assistance from Pasco Corporation and coordinated by the Forestry Commission of Ghana, focused on land use and forest resource baseline mapping, GIS-based forest inventory system development, carbon stock assessment and capacity building. The LAMP approach was applied to estimate carbon from all five carbon pools following the IPCC guidelines. These carbon pools include above-ground, below-ground, deadwood, litter and soil, over a sub-national pilot area of 1.7 million hectares. The assessment provided emission factors by forest types and the results had already contributed to the Global Forest Resource Assessment (FRA 2015) and development of the forest reference emission levels of Ghana.

The target of the project was to produce a high-resolution LiDAR-based carbon stock map for 2.3 million hectares of landscape and establish a reference scenario for sub-national forest carbon project development. Arbonaut managed LiDAR data acquisition, sampling design and calculating carbon stock for above- and below-ground biomass. The success of this project allowed Nepal to access the World Bank’s Forest Carbon Partnership Facility.

Vesinetti was an online platform where research and monitoring information on lakes, rivers and coastal areas is exchanged between officials and water management networks. Uploaded data can be used to generate HTML pages with the option to share a link, therefore enabling the use of the service for the general public interested in the topic. The project, which is implemented within the framework of the EU LIFE program, was based on extensive cooperation. More than 70 scientists and experts as well as local operators had een participating in the cooperation under the guidance of the Finnish Environment Institute.

Arbonaut consulted Indufor Ltd in the framework of the FRA Nepal Project. Assignments included several services regarding the development of a LiDAR team, planning and organizing research activities and pilot studies to develop new methodologies, and also supervision and participation in processing, interpreting and use of the airborne laser scanning data.

The Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Norway and Arbonaut signed a consultancy contract concerning the National Carbon Monitoring Centre in Tanzania. A team of seven consultants was assigned to review existing initiatives, carry out stakeholder consultation and prepare a Programme Document for the establishment of a National Carbon Monitoring Centre for Tanzania.

PaikkaOppi was a web-based learning environment designed to support geography, geographic information and environmental research education at primary and secondary schools. This learning environment offered diverse tools, data and tasks for teaching the basics of geographic information and studying the environment (vicinity) with a GIS methodology. The system allowed students to acquire geographic information layers from different sources over standard interfaces and to prepare statistical and thematic maps. Besides students could digitize and add some of their own objects, attachments and comments into the database, share the contents with a wider audience, and publish prepared workbooks.

Arbonaut successfully carried out management-level forest inventories covering more than 5 million hectares in Finland for the needs of public and private institutions including the Finnish Forest Centre, Metsähallitus, UPM, and Tornator. Assignments included field data sample design and collection, automatic stand delineation, and estimation of forest attributes on stand- and grid-levels, based on LiDAR data and aerial imagery.
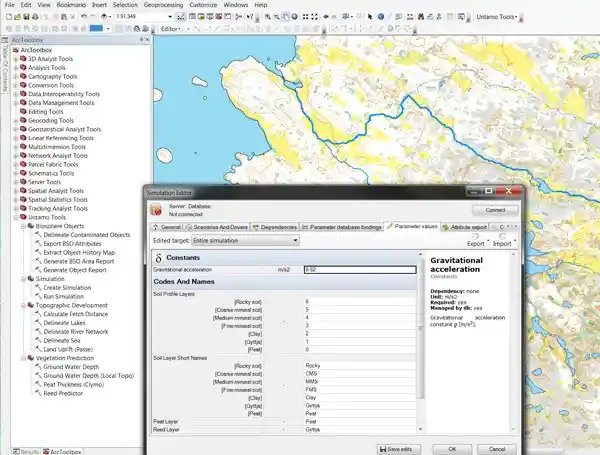
Untamo Tools toolbox implemented models for predicting likely outcomes of processes that drive changes in the terrain, surface, and underground water bodies, sedimentation, vegetation, and human habitats, to name a few. Multiple scenarios were defined to address uncertainties in long-term development paths, such as changes in the climate or human impact on the biosphere. Together, full automation and reliable auditing are the keys to carrying out assessment simulations successfully, traceably, and in a quality-controlled manner.





